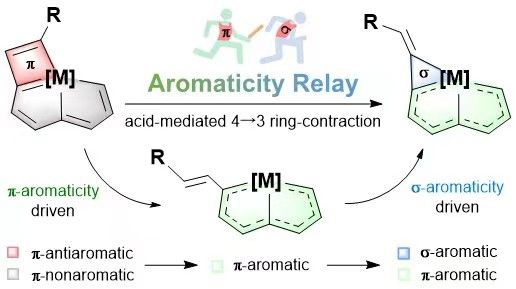
π-Aromaticity is an important driving force in directing the synthesis of aromatic compounds; in contrast, reactions induced by σ-aromaticity are uncommon. Here we report a strategy based on π- and σ-aromaticity relays to realize the structurally defined ring contraction of metallacyclobutadiene to metallacyclopropene. This reaction involves the release of the π-antiaromaticity of metallacyclobutadiene to afford a π-aromatic intermediate, followed by ring reclosure to generate σ-aromatic metallacyclopropene. The ring opening–reclosing mechanism and versatile switching of the aromaticity of the metallacyclic species are supported by experimental results and theoretical calculations. This work demonstrates the importance of aromaticity relay with the successive decrease of energy in reactions and will stimulate efforts in exploiting the vital role of aromaticity in synthetic chemistry.
URL link for Article https://www.nature.com/articles/s44160-022-00194-2